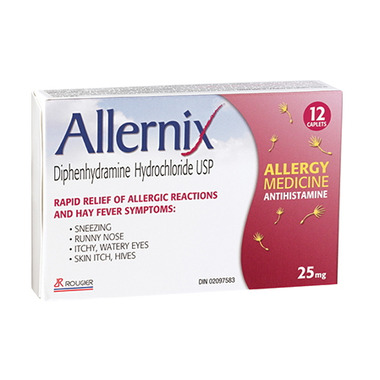
Uses
Diphenhydramine is an antihistamine, antiemetic and antispasmodic. The use of this medicine is recommended for the treatment of allergic diseases such as hay fever, angioedema, contact dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, pruritus, gastrointestinal allergies, physical allergies, allergic transfusion reactions, reactions to infection of contrast media, and reactions to therapeutic preparations. It is also recommended for postoperative nausea and vomiting, motion sickness and emotionally disturbed children. When this medicine is used for motion sickness, it has to be administered 30 minutes before the event that may cause the motion sickness and preferably 1 or 2 hours before.
Dosage/Directions for use
Oral: Caplets: Adults: 25 to 50 mg, 3 or 4 times a day. Children, 10 to 12 years old: 25 mg, 3 to 4 times a day or as prescribed. These caplets are not recommended for children under 10.
Ingredients
Caplets 50 mg: Each white, coated caplet contains 50 mg of diphenhydramine hydrochloride USP. Also contains Opraspray White K-17000 as a coloring agent. Gluten, lactose, paraben, sodium, sulfite, tartrazine and sucrose free. Sweetened with sorbitol.
Precautions
This medicine can not be used for a prolonged treatment and the recommended dose should not be exceeded except as directed by a physician. When this medicine is administered to patients suffering from a narrowangle glaucoma, stenosing peptic ulcer, pyloroduodenal obstruction, asthma, symptomatic prostatic hypertrophy or bladder neck obstruction, it has to be done with considerable caution. Not recommended for children with chronic lung disease or glaucoma. Use in Children: When there is an overdosage of antihistamines in infants and children, it may cause hallucinations and convulsions and it might also result in the death of the patient. In children, the mental alertness may be diminished by antihistamines and in young children they may cause excitation. Geriatrics: In persons 60 years of age and older, drowsiness, dizziness, sedation and hypotension are more susceptible to be caused by antihistamines. Pregnancy and lactation: In pregnancy and lactation, the safety for use has not been determined yet. Small quantities of antihistamines have been found in breast milk, the use of this medicine is therefore not recommended during lactation because very young children are more sensible to adverse effects of antihistamines such as excitement and irritability. Antihistamines also have the tendency to reduce the body secretions, it is therefore possible that the flow of breast milk would be reduced in some patients.
Highlights
- We are only able to ship this item to Canadian customers.